Marketing Communication. Capital at risk. For Professional Investors Only.
Artificial intelligence has dominated headlines for creativity and its ability to generate text, images, and code. Yet the next wave of disruption may not be digital at all, it could be physical. Robotics represents the physical embodiment of AI, where algorithms are given arms, legs, and sensors to act in the real world. This fusion of intelligence and machinery is happening faster than expected. From Amazon’s warehouses to hospital operating rooms, robots are moving beyond repetitive tasks to adaptive, complex functions once reserved for humans. Costs are declining, capabilities are rising, and entire industries from semiconductors to healthcare are being reshaped in the process. The robotics theme is transitioning from a long-term vision to a near-term reality, creating potential opportunities across manufacturing, hardware, software, and AI integration.
Key takeaways:
Artificial intelligence has primarily existed in the digital realm, shaping data, language, and decision systems. Robotics represents the next frontier, embedding AI into the physical world through “agents” that can see, move, and act.4 Advances in Visual-Language-Action (VLA) models exemplify this shift, giving robots the ability to perceive their surroundings in three dimensions, differentiate non-uniform objects, and apply the correct amount of force when manipulating goods.5
Amazon’s Vulcan robot represents a potential breakthrough in warehouse automation, moving beyond speed and dexterity to something more humanlike, the ability to feel.6 Unlike earlier “numb and dumb” machines, Vulcan uses robotic arms from Teradyne’s Universal Robots division that integrate advanced tactile sensors and force feedback systems.7 These allow the robot to gauge pressure, adjust grip, and handle irregular or delicate items without damage.8 Teradyne’s role underscores how the humanoid supply chain spans robotic arms, sensors, AI chips, and software integration. Combined with visual-language-action models that enable three-dimensional reasoning, Vulcan can now perform picking and stowing tasks once considered nearly impossible to automate.9 Amazon now deploys more than 750,000 robots across over 20 models in its facilities a scale that suggests robots could soon outnumber human employees in its warehouses.10
At Automatica 2025, ABB Ltd showcased its Autonomous Versatile Robotics vision, introducing AI-powered mobile robots that can plan and execute tasks independently, switching between operations in real time without human guidance.11 The company also expanded its large robot lineup with the IRB 6730S, a high-payload shelf-mounted robot, and the IRB 6760, a high-speed press-tending robot, both offering precise, energy-efficient performance.12
In the medical technology sector Intuitive Surgical Inc. continues to lead in robotic-assisted surgery with its latest advancement, the da Vinci 5 Surgical System, providing surgeons with real-time insights, including an integrated force gauge and in-console video replay, aimed at improving precision and efficiency in complex procedures.13 The force gauge measures the pressure applied by robotic instruments during surgery, providing surgeons with real-time tactile feedback to prevent tissue damage and enhance precision in delicate procedures like cardiovascular or urological operations.14 The company has also showcased telesurgery capabilities, allowing surgeons to perform operations remotely and highlighting the growing potential of connected, next-generation surgical interventions.15
The transformation of robotics from rigid, pre-programmed machines into adaptive, intelligent systems is being driven by the integration of AI software frameworks, powerful edge computing, and advanced sensors.16 Nvidia appears to be at the centre of this evolution. Its robotics stack has attracted over two million developers and now supports more than 7,000 enterprise customers.17 The company recently introduced its Jetson Thor platform, which targets humanoid and industrial robots with a comprehensive suite of solutions, from generative AI models to simulation environments like Isaac, the GR00T humanoid baseline, Metropolis visual AI, and Holoscan for real-time sensor processing.18 Nvidia’s ecosystem has grown into more than 150 hardware, software, and sensor partners, effectively providing a turnkey “full-stack” pathway for robotics developers.19
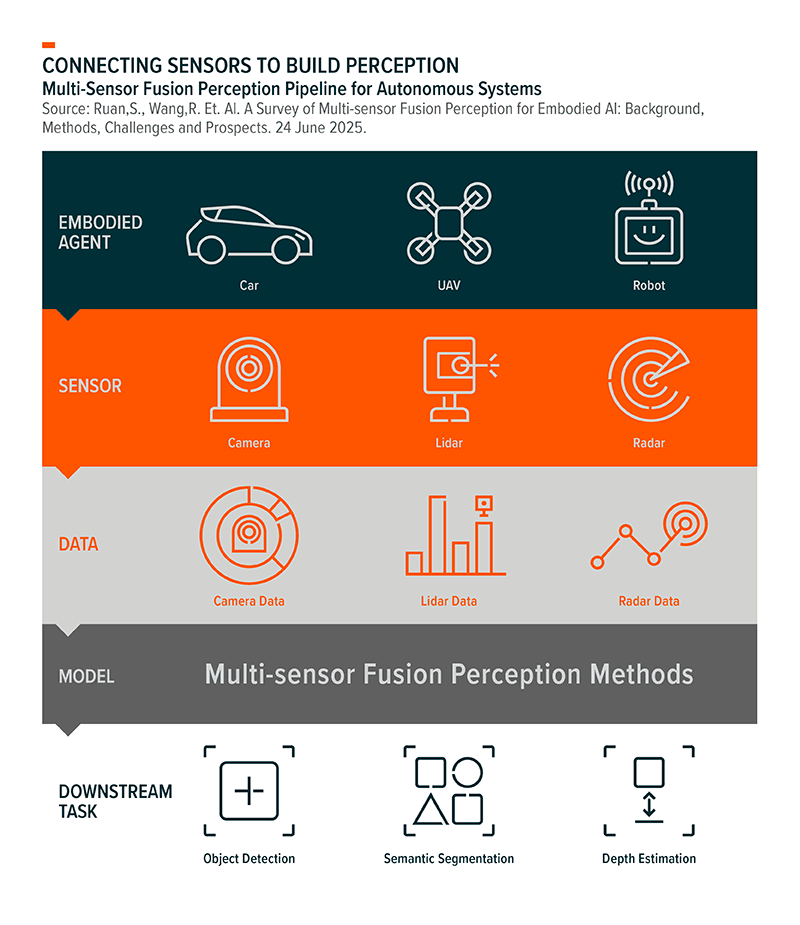
Meanwhile, sensor innovation is expanding the capabilities of robots. Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) is a sensing technology that emits laser pulses, measures the time for the light to bounce back, and uses that data to build precise 3D point clouds of the environment, enabling robots to perceive distance, shape, obstacles, and terrain.20 LiDAR and advanced perception technologies are enabling machines to map, navigate, and interact with complex environments in real time, opening new applications across smart infrastructure, autonomous mobility, and industrial settings.21 In the construction of embodied AI systems, sensor data understanding is the core link between the physical world and digital intelligence.22
Hesai Group sells LiDAR sensors and recently secured a design win with Toyota for its long-range “ATX” LiDAR sensor, to be used in vehicles made by a Toyota joint venture in China, with mass production slated for 2026.23 Similarly RoboSense Technology Co. launched new robotics vision products like the Active Camera (AC1) series, which fuse LiDAR, cameras, and IMU sensors into a more integrated perception system for robots, enabling applications such as navigation, object detection, and autonomous operation.24
Ouster Inc. another player in the LiDAR sensor market also announced a strategic partnership with Constellis (formerly U.S. private military company Blackwater security) to integrate its “Gemini” digital LiDAR and software stack into advanced security and situational awareness solutions.25 This collaboration extends Ouster's applications beyond autonomous vehicles to environments such as facility security and mission support, enhancing real-time 3D situational awareness and object tracking across challenging weather and light conditions.26
As these sensing technologies scale from prototype to mass deployment, unit economics improve, and robotics adoption accelerates. Healthcare is one of the most promising beneficiaries. The global medical robotics market, currently valued at about $8 billion, is expected to surpass $30 billion by 2031.27 Surgical robotics dominates the space today, but rehabilitation and hospital automation systems are growing quickly as hospitals seek to enhance precision, safety, and efficiency.28
Taken together, these advances could be transforming robotics into a multi-dimensional technology platform. What began as single-purpose machines is now evolving into intelligent, networked systems capable of learning, adapting, and working seamlessly alongside human operators across manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and beyond.
Perhaps the most striking development in robotics today is the accelerating timeline for humanoid deployment. Once thought to be decades away, humanoids are now expected to see meaningful industrial and even household adoption within the next three to four years.29 This acceleration is being driven by embodied AI, the application of large language models, reinforcement learning, and generative AI to physical machines, combined with declining costs and early industrial deployments.30 Entry-level humanoid platforms are already approaching price points below $20,000, opening the door to broader adoption.31
Startups and established companies alike are making strides. 1X, led by roboticist Bernt Børnich, introduced its humanoid NEO as a household assistant capable of vacuuming, watering plants, and providing company.32,33 Børnich describes NEO as part of a vision for robotic helpers that take over routine chores, freeing people to focus on higher-value pursuits.
Unitree Robotics is driving broader adoption of humanoid robots with its G1 priced at $16,000 and R1 priced at $5,900 models.34,35 These robots use embodied AI, combining reinforcement learning and large language models for real-time interaction.36 The G1 offers 23 degrees of freedom for complex movements like walking, jumping, and object manipulation, while the R1 provides an affordable entry point.37 Falling costs and these capabilities are making humanoid robots increasingly accessible for research, education, and industrial use. Unitree’s G1 humanoid, priced at $16,000 versus $500,000 industrial models in 2023, highlights a dramatic cost drop that signals robots are entering a Moore’s Law–style cost curve, with Unitree’s breakthrough suggesting others will soon follow.38
Crucially, Nvidia’s partnership with Foxconn signals that humanoid production is no longer a distant concept.39 Humanoid production is scheduled to begin in the U.S. by early 2026, with Blackwell Ultra GB300 AI servers supplying the compute capacity needed for industrial training scenarios.40 This represents a potential major step in moving robots from research labs to factory floors and eventually into homes.
As humanoids move from factories into homes, the economic implications extend beyond productivity. Cloud infrastructure and data management providers are expected to benefit from the surge in custom AI models required for consumer-based humanoids, generating significant new demand for compute and storage resources.41 Investors can also look to key enablers across sensors, IoT systems, and machine learning tools that enhance humanoid capability. Ultimately, humanoids represent a new phase of robotics adoption: one that may not only transform industrial efficiency and supply chain resilience, but also potentially reshapes the daily lives of individuals by integrating “physical AI” into everyday routines.
The robotics story is no longer confined to factory automation or industrial assembly lines. It is evolving into a platform technology, one that combines AI software, advanced sensors, and embodied intelligence to transform how economies function and how individuals live. As reshoring intensifies and labour markets tighten, robotics is emerging as a critical lever for productivity and competitiveness. For investors, this means exposure to robotics is not simply a bet on automation, but on the rise of “physical AI” as a defining technology of the next decade.
1. He, J. Vertical Applications of Multi-modal Sensor Fusion: A Comparative Study of Medical Robots and Industrial Robots. 19 May 2025.
2. Tahir, N. Edge Computing and Its Application in Robotics: A survey. 23 June 2025.
3. Wang, J., et all. Embracing the future: the rise of humanoid robots and embodied AI. 19 May 2024.
4. World Economic Forum. Physical AI: Powering the New Age of Industrial Operations. September 2025.
5. Ud Din, M., Akram,Waseem. Cornell University. Vision Language Action Models in Robotic Manipulation: A Systematic Review. 14 July 2025.
6. Amazon. Introducing Vulcan: Amazon's first robot with a sense of touch. 7 May 2025.
7. Ibid.
8. Ibid.
9. Ibid.
10. Ibid.
11. ABB. ABB showcases path to new era of Autonomous Versatile Robotics at automatica 2025. 24 June 2025
12. Ibid.
13. Intuitive Surgical. Intuitive Introduces Real-Time Surgical Insights for da Vinci 5. 12 September 2025.
14. Ibid.
15. Ibid.
16. Forbes. How Physical AI Transforms Industries Through Embedded Intelligence. 3 May 2025.
17. NVIDIA. Nvidia Blackwell-Powered Jetson Thor Now Available, Accelerating the Age of General Robotics. 25 August 2025.
18. Ibid.
19. Ibid.
20. Synopsis. What is LiDAR?. Accessed 15 September 2025.
21. Patil, A., et all. Bulding the Future of Transportation: A comprehensive Survey on AV Perception, Localization, and Mapping. 23 March 2025.
22. Ruan,S., Wang,R., A Survey of Multi-sensor Fusion Perception for Embodied AI: Background, Methods, Challenges and Prospects. 24 June 2025.
23. Hesai. Hesai Secures New Lidar Design Win from Toyota. 15 August 2025.
24. PR Newswire. RoboSense Launches AC1: The All-in-One AI-Powered Robotic Vision Platform. 28 March 2025.
25. BusinessWire. Ouster Announces Strategic Partnership with Constellis to Bring Physical AI to Advanced Security Operations. 15 September 2025.
26. Ibid.
27. SkyQuest Technology. Medical Robots Market to Witness Massive Growth at USD 34.32 Billion by 2031. 29 November 2024.
28. Ibid.
29. Goldstein, S., MarketWatch. 300 million humanoid robots are coming — and here are the companies that will benefit. 18 June 2025.
30. Perez, L., PAL. The rise of embodied AI: Robots that learn by doing. 18 June, 2025.
31. Top 3D Shop. Humanoid Robots Guide (2025): Types, History, Best Models, Anatomy and Applications.28 April 2025.
32. Freethink. Humanoid helpers are now entering our homes. 15 March 2025.
33. TedTalks. Meet NEO, your robot butler in training. April 2025.
34. Reuters. China's Unitree prices new humanoid robot at deep discount to 2024 model. 25 July 2025.
35. Unitree Website. Accessed 15 September 2025.
36. The Verge. You’ll need to teach this $16,000 humanoid robot how to make breakfast 19 August 2024.
37. Ibid.
38. Citrini Research. Thematic Primer: Humanoid Robots. 16 May 2025.
39. Reuters. Nvidia, Foxconn in talks to deploy humanoid robots at Houston AI server making plant. 20 June 2025.
40. Ibid.
41. NVIDIA. NVIDIA Powers Humanoid Robot Industry With Cloud-to-Robot Computing Platforms for Physical AI. 19 May 2025.